Best website to buy domain – Finding the best website to buy a domain is crucial for establishing your online presence. Your domain name is your digital address, acting as the foundation for your website and brand identity. A well-chosen domain name can attract visitors, build trust, and contribute to your online success.
Navigating the world of domain registrars can be overwhelming, with numerous options and features to consider. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of factors to evaluate, popular domain registrars, and essential tips for securing your ideal domain name.
Introduction: Best Website To Buy Domain
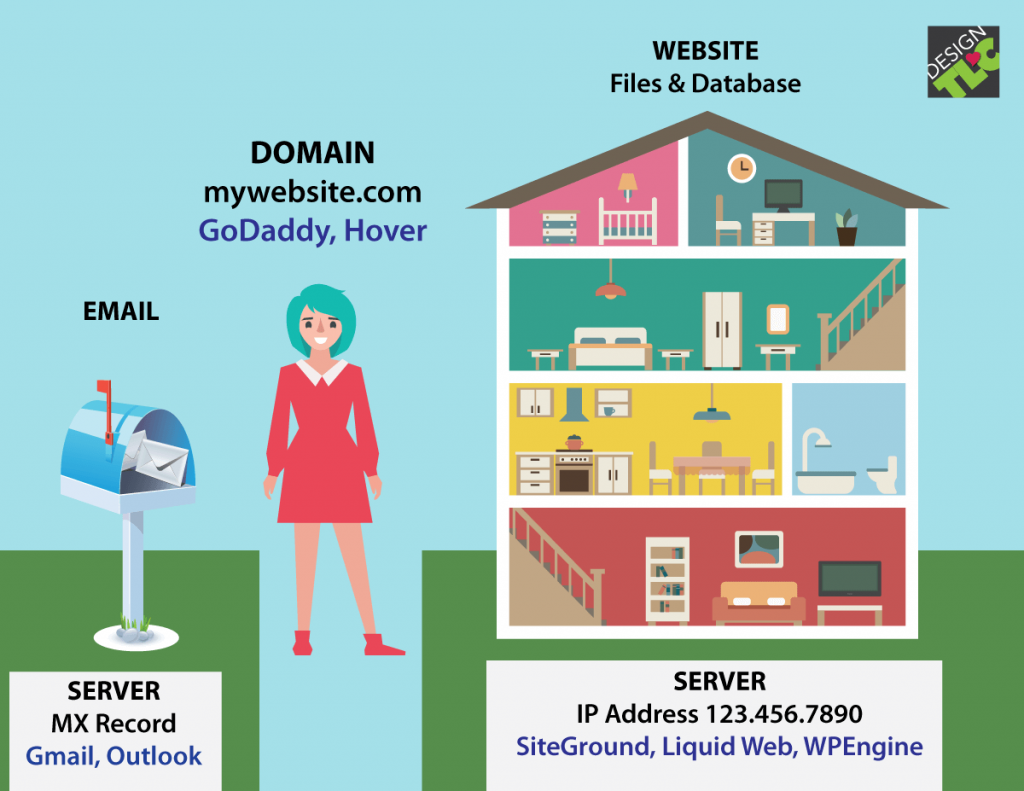
A domain name is your website’s unique address on the internet, like a physical address for your online presence. It’s what people type into their web browsers to access your website.
Choosing the right domain name is crucial for your website’s success. A good domain name is memorable, relevant to your website’s content, and easy to spell and pronounce. It can influence your website’s branding, credibility, and search engine optimization ().
Importance of Choosing the Right Domain Name
A well-chosen domain name can offer several advantages:
- Improved Brand Recognition: A memorable and relevant domain name can help your website stand out and become easily recognizable by your target audience. For example, “Amazon.com” is instantly associated with online shopping.
- Enhanced Credibility: A professional-sounding domain name can build trust and credibility with your visitors. A domain name like “yourbusiness.com” conveys a sense of legitimacy compared to a random string of characters.
- Better : A domain name that includes relevant s can improve your website’s ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). For example, a website selling shoes might benefit from a domain name like “shoestore.com”.
- Increased Traffic: A memorable and easy-to-remember domain name can lead to more people visiting your website, as it’s easier for them to share and recommend it to others.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Domain Registrar
Choosing the right domain registrar is crucial for securing your online presence and ensuring a smooth experience. A domain registrar is responsible for managing your domain name, making it essential to choose a reliable and trustworthy provider. Several factors should be considered when selecting a domain registrar.
Domain Name Availability
Domain name availability is paramount. Before selecting a registrar, it’s essential to ensure your desired domain name is available. Many registrars offer domain name search tools that allow you to check availability instantly. If your desired name is already taken, you can explore alternative options or use a domain name generator to suggest similar names.
Pricing
Domain registration fees can vary significantly between registrars. It’s essential to compare prices from different providers to find the best value for your money. While lower prices might seem appealing, it’s crucial to consider the overall value offered, including features and customer support. Look for registrars that offer competitive pricing for domain renewals and additional services like website hosting and email accounts.
Customer Support
Reliable customer support is vital, especially if you encounter issues with your domain name or require assistance with technical aspects. Look for registrars with readily available customer support channels, such as phone, email, and live chat. Evaluate their responsiveness, helpfulness, and ability to resolve issues effectively.
Domain Privacy and Security
Domain privacy and security are crucial to protect your personal information from public disclosure. Some registrars offer domain privacy protection services that hide your contact information from public WHOIS databases. This feature is essential for safeguarding your privacy and preventing spam or unsolicited contact. Additionally, choose a registrar that employs strong security measures to protect your domain name and personal data from unauthorized access.
Domain Name Extensions (TLDs)

Domain name extensions, also known as top-level domains (TLDs), are the suffixes that come after the dot (.) in a website address. They play a crucial role in defining the purpose and nature of a website. While the .com extension is widely recognized, a variety of other TLDs cater to different needs and industries. Choosing the right TLD can enhance your brand identity, target specific audiences, and improve your website’s .
Popular Domain Name Extensions
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of different TLDs is essential for choosing the best one for your website.
- .com: The most popular and widely recognized TLD, suitable for businesses, personal websites, and various online ventures. Its general nature makes it universally acceptable and easy to remember.
- .net: Originally intended for network-related websites, .net has become a popular choice for businesses and individuals seeking a professional and trustworthy online presence. It’s often seen as a good alternative to .com if the desired .com domain is unavailable.
- .org: Primarily used by non-profit organizations, educational institutions, and community groups. It signifies a focus on social good and public benefit.
- .io: A popular choice for technology-related websites, startups, and businesses operating in the tech sector. It’s associated with innovation and agility.
- .co: A country-code TLD for Colombia, but it has gained popularity as a generic TLD, often used by businesses and startups seeking a concise and memorable domain name.
- .info: Designed for informational websites, .info is suitable for blogs, news sites, and websites offering factual information. It’s often chosen for its descriptive nature.
- .biz: Specifically designed for businesses, .biz is a good option for companies looking for a professional and trustworthy online presence. It’s often seen as an alternative to .com for business websites.
- .me: Originally intended for personal websites, .me has become popular for bloggers, artists, and individuals seeking a unique online identity. It’s often used to showcase personal projects and creative work.
Choosing the Right TLD
The choice of TLD depends on various factors, including the type of website, target audience, and brand identity.
- Brand Identity: Certain TLDs are associated with specific industries or values. For example, .org suggests a non-profit organization, while .io is commonly associated with technology startups.
- Target Audience: Consider your target audience and their expectations. If you’re targeting a global audience, .com is generally the best choice. However, if you’re targeting a specific region or industry, a country-code TLD or an industry-specific TLD might be more appropriate.
- Considerations: While TLDs don’t directly impact ranking, they can influence brand perception and user trust. Choosing a relevant and recognizable TLD can contribute to a positive user experience and improve your website’s overall performance.
- Availability: Check the availability of your desired domain name across different TLDs. If your preferred .com domain is unavailable, consider alternative TLDs that align with your brand and target audience.
Domain Name Management
Once you’ve chosen and registered your domain name, it’s essential to manage it effectively. Domain name management encompasses various tasks that ensure your domain functions correctly and remains under your control.
Updating Contact Information
Keeping your contact information up-to-date is crucial for several reasons. First, it allows domain registrars to reach you with important updates, notifications, and renewal reminders. Second, accurate contact information ensures you receive critical security alerts, such as potential domain hijacking attempts.
- Name: Ensure your full legal name is accurate and matches the information on your identification documents.
- Email Address: This is the primary way registrars communicate with you. Use a reliable email address you check regularly.
- Phone Number: Provide a valid phone number where you can be reached. This is essential for security purposes, especially in case of domain transfers or disputes.
- Address: Ensure your physical address is current. This information is used for legal notices and other important communications.
Setting Up DNS Records
DNS (Domain Name System) records are like a phone book for your website. They connect your domain name to the actual server where your website files are stored.
- A Records: Map your domain name to the IP address of your web server.
- CNAME Records: Create aliases for your domain name. For example, you can create a CNAME record to point “www.yourdomain.com” to “yourdomain.com”.
- MX Records: Direct email sent to your domain to the appropriate email server.
- TXT Records: Used for various purposes, including email authentication and domain verification.
Renewing Your Domain, Best website to buy domain
Domain names are typically registered for a period of one to ten years. When your registration period expires, you need to renew it to prevent your domain from lapsing.
- Renewal Reminders: Most domain registrars send renewal reminders well in advance of the expiration date.
- Automatic Renewal: Some registrars offer automatic renewal options. This ensures your domain is automatically renewed without you having to manually take action. However, be sure to review the terms and conditions to avoid unexpected charges.
- Renewal Grace Period: If you miss the renewal deadline, you may have a grace period to renew your domain. However, during this period, your domain may be placed on hold, and you might incur additional fees.
Domain Name Disputes and Resolutions
Domain name disputes can arise when two or more parties claim ownership of the same or similar domain name. These disputes can be complex and involve various legal and ethical considerations. Understanding the potential causes and resolution processes for domain name disputes is crucial for protecting your intellectual property and ensuring the smooth operation of your online presence.
Domain Name Dispute Resolution
Domain name disputes are typically resolved through a formal process involving an independent third-party organization. One of the most recognized organizations for resolving domain name disputes is the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). WIPO administers the Uniform Domain-Name Dispute-Resolution Policy (UDRP), which provides a framework for resolving disputes related to domain names registered under the .com, .net, and .org top-level domains (TLDs).
The UDRP process offers a relatively quick and cost-effective alternative to traditional litigation. It is designed to address disputes involving domain names that are:
- Identical or confusingly similar to a trademark or service mark.
- Registered in bad faith.
- Used in bad faith.
The UDRP Process
The UDRP process involves the following steps:
- Complaint Filing: The complainant, who alleges that the domain name is in violation of their rights, files a complaint with a WIPO-approved dispute resolution provider. The complaint must include specific details about the domain name in dispute, the complainant’s rights, and evidence supporting their claim.
- Response: The respondent, who is the owner of the disputed domain name, has 20 days to respond to the complaint. The response can either be an admission of wrongdoing or a denial of the allegations.
- Panel Decision: A panel of independent experts, chosen from a list of accredited panelists, reviews the complaint, the response, and any supporting evidence. The panel then issues a decision, which can be one of the following:
- Transfer: The panel orders the transfer of the disputed domain name to the complainant.
- Cancellation: The panel orders the cancellation of the disputed domain name.
- Dismissal: The panel dismisses the complaint, finding that the complainant has not met the requirements of the UDRP.
Factors Affecting UDRP Outcomes
The outcome of a UDRP case is determined by the panel’s assessment of the evidence and arguments presented by both parties. Some key factors that influence the panel’s decision include:
- Strength of the Complainant’s Trademark Rights: The panel will consider the strength of the complainant’s trademark or service mark, including its distinctiveness, reputation, and prior use.
- Similarity of the Domain Name to the Trademark: The panel will assess the similarity between the disputed domain name and the complainant’s trademark. A high degree of similarity is more likely to result in a finding of bad faith registration or use.
- Respondent’s Intent: The panel will consider the respondent’s intent in registering and using the disputed domain name. If the respondent registered the domain name with the intention of profiting from the complainant’s trademark or reputation, this is likely to be considered bad faith.
- Respondent’s Use of the Domain Name: The panel will consider the respondent’s use of the disputed domain name. If the domain name is being used to sell goods or services that are confusingly similar to the complainant’s goods or services, this is likely to be considered bad faith use.
Ultimate Conclusion
Choosing the right domain registrar is a significant step in building your online presence. By understanding the key factors, comparing popular options, and following best practices, you can secure a domain name that reflects your brand, enhances your website’s credibility, and sets you up for online success.