Server host, the unseen backbone of every website and online application, plays a pivotal role in the digital world. From humble personal blogs to sprawling e-commerce platforms, a reliable server host ensures seamless functionality and accessibility. Understanding the different types of server hosts, their features, and how to choose the right one is crucial for building a successful online presence.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of server hosting, providing insights into various hosting options, setup and configuration, management, security, performance optimization, scalability, cost considerations, and industry trends. Whether you’re a seasoned web developer or a novice website owner, this guide will equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the world of server hosting and make informed decisions for your online ventures.
Server Host Basics
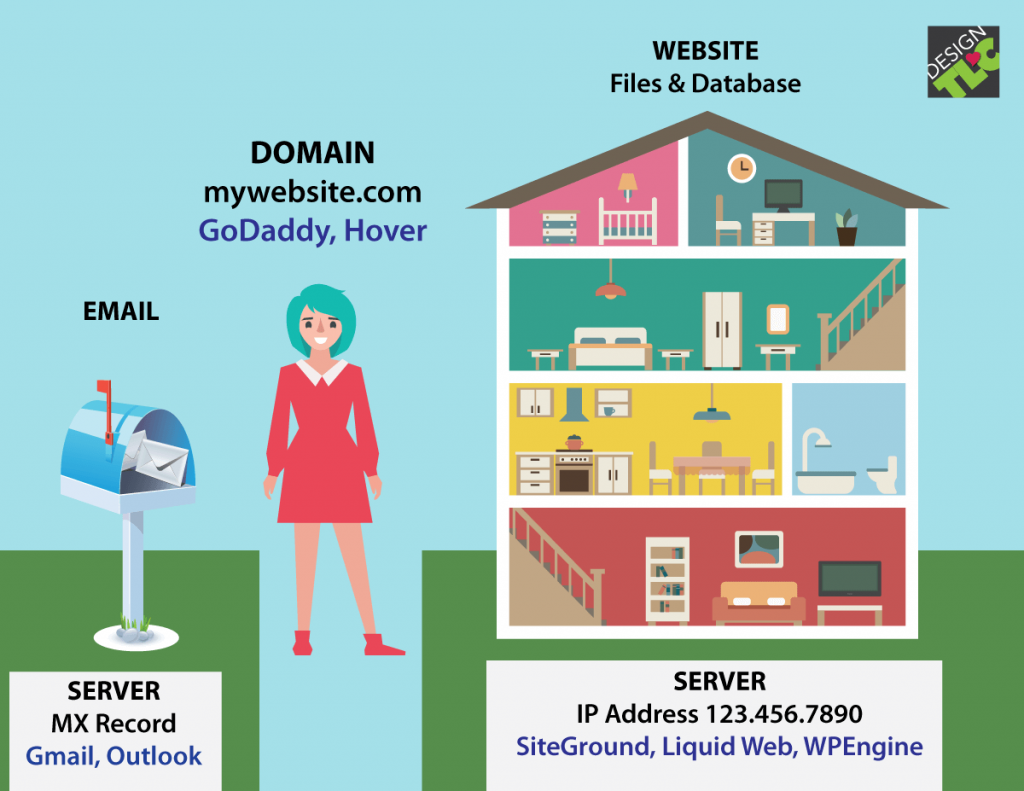
A server host, often referred to as a web hosting provider, plays a crucial role in the online world by providing the infrastructure necessary to host websites and web applications. Think of it as the physical or virtual space where your website lives and can be accessed by users worldwide.
Types of Server Hosts
Different types of server hosts cater to varying needs and budgets. The choice depends on factors like website traffic, resource requirements, and desired level of control.
- Shared Hosting: The most affordable option, where multiple websites share the same server resources. It’s suitable for low-traffic websites with basic needs.
- VPS (Virtual Private Server): Offers more resources and control than shared hosting. A virtualized server environment provides dedicated resources, making it suitable for medium-traffic websites with moderate resource requirements.
- Dedicated Server: Provides exclusive access to an entire physical server, offering maximum control and performance. It’s ideal for high-traffic websites, demanding applications, or businesses requiring a high level of security.
- Cloud Hosting: A scalable and flexible option that utilizes a network of servers to distribute resources. It’s suitable for websites with fluctuating traffic and resource needs, offering high availability and redundancy.
Key Features and Benefits of Different Server Hosts
Each type of server host comes with distinct features and benefits that align with specific needs.
Shared Hosting
- Cost-Effective: Shared hosting is the most budget-friendly option, making it ideal for small businesses and personal websites with low traffic.
- Ease of Use: Many shared hosting providers offer user-friendly control panels and automated setup processes, simplifying website management.
- Limited Resources: Shared hosting environments share resources with other websites, potentially leading to performance issues if one website experiences high traffic or resource demands.
VPS Hosting
- Enhanced Performance: VPS hosting provides dedicated resources, leading to improved website speed and responsiveness compared to shared hosting.
- Increased Control: VPS users have more control over their server environment, allowing for customization and installation of specific software.
- Higher Cost: VPS hosting is more expensive than shared hosting, but it offers a significant performance and control advantage.
Dedicated Server Hosting
- Ultimate Control: Dedicated server hosting provides complete control over the server environment, allowing for customization and optimization for specific applications.
- Maximum Performance: Dedicated servers offer the highest performance and reliability, making them suitable for high-traffic websites and resource-intensive applications.
- High Cost: Dedicated servers are the most expensive hosting option, requiring significant investment in hardware and maintenance.
Cloud Hosting
- Scalability: Cloud hosting allows for easy scaling of resources based on traffic fluctuations, ensuring optimal performance and availability.
- High Availability: Cloud hosting utilizes a network of servers, ensuring website uptime even if one server experiences issues.
- Flexibility: Cloud hosting offers flexibility in terms of operating systems, software, and configurations, catering to diverse needs.
Choosing the Right Server Host
Choosing the right server host is crucial for the success of your website or application. A well-chosen host provides a stable and reliable platform for your online presence, ensuring optimal performance and user experience.
Factors to Consider
Several key factors influence your decision when selecting a server host. Understanding these factors helps you make an informed choice that aligns with your specific needs and budget.
- Website Traffic: The amount of traffic your website receives is a significant factor in determining the resources required. High-traffic websites necessitate robust hosting solutions with ample bandwidth and processing power to handle the increased load.
- Resource Requirements: Your website’s specific resource requirements, such as storage space, RAM, and CPU power, play a crucial role in choosing the right hosting plan. Complex applications or websites with large media files demand higher resource allocation.
- Budget: Hosting costs vary widely based on the features, resources, and level of support offered. Establishing a clear budget helps narrow down options and find a host that fits your financial constraints.
- Technical Expertise: Your technical expertise influences the level of control and management you require. If you lack technical skills, a managed hosting solution with dedicated support may be ideal.
Evaluating Hosting Providers
Once you understand your needs, it’s time to evaluate different hosting providers. Here are some practical tips for comparing their services:
- Read Reviews: Explore online reviews and testimonials from other users to gain insights into a provider’s reputation, performance, and customer service.
- Compare Features: Compare the features offered by different providers, such as storage space, bandwidth, databases, and security measures. Ensure they align with your website’s specific requirements.
- Check Uptime Guarantees: Look for providers with high uptime guarantees, ideally exceeding 99.9%. This ensures your website remains accessible to visitors most of the time.
- Evaluate Customer Support: Assess the availability and responsiveness of customer support. Look for providers offering 24/7 support through various channels, such as phone, email, and live chat.
Security Features
Security is paramount when choosing a server host. Look for providers offering robust security features to protect your website and data from threats:
- SSL Certificates: Ensure the host provides free SSL certificates for encrypting data transmission between your website and visitors, enhancing security and trust.
- Firewalls: A robust firewall protects your server from unauthorized access and malicious attacks, safeguarding your website and data.
- Regular Security Updates: The host should proactively update its servers and software with the latest security patches to mitigate vulnerabilities and keep your website protected.
- Malware Scanning: Regular malware scanning helps detect and remove any malicious code that may compromise your website’s security.
Uptime Guarantees
Website uptime is crucial for user experience and search engine rankings. A reliable server host provides high uptime guarantees, ensuring your website remains accessible to visitors:
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Look for providers with clear SLAs that specify uptime guarantees and penalties for downtime. This provides legal recourse in case of service disruptions.
- Redundant Infrastructure: Reputable hosts invest in redundant infrastructure, such as multiple servers and data centers, to minimize downtime in case of hardware failures.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential for identifying and resolving potential issues before they affect your website’s availability.
Customer Support
Reliable customer support is vital for resolving technical issues and ensuring a smooth hosting experience:
- 24/7 Availability: Choose a host offering 24/7 customer support through multiple channels, including phone, email, and live chat, to address issues promptly.
- Knowledge Base and Documentation: A comprehensive knowledge base and documentation provide valuable resources for troubleshooting common issues and finding solutions independently.
- Response Time and Resolution: Evaluate the host’s response time to inquiries and their ability to resolve issues effectively. Look for providers with a proven track record of timely and efficient support.
Server Host Setup and Configuration
Setting up and configuring a server host involves a series of steps that ensure your website or application runs smoothly and securely. This process involves acquiring a domain name, creating an account with a server host, and transferring files to the server. You’ll also need to configure various settings, such as database management, security protocols, and email accounts.
Domain Name Registration
Before setting up a server host, you need a domain name. This is the address that users will type into their web browsers to access your website. Here’s how to register a domain name:
- Choose a domain registrar: There are many domain registrars available, such as GoDaddy, Namecheap, and Google Domains. Select one that offers the features and pricing that best suit your needs.
- Search for available domain names: Once you’ve chosen a registrar, search for available domain names that are relevant to your website or application. It’s important to choose a domain name that is easy to remember and relevant to your content.
- Register your domain name: Once you’ve found an available domain name, register it with the registrar. This usually involves paying a fee, which can vary depending on the domain name extension (e.g., .com, .net, .org) and the registrar.
Account Creation
After registering your domain name, you need to create an account with your chosen server host. This process usually involves providing personal information, choosing a hosting plan, and setting up payment details.
- Choose a hosting plan: Server hosts offer various hosting plans, each with different features and resources. Consider your website’s traffic, storage requirements, and other needs when selecting a plan.
- Provide personal information: You’ll need to provide your name, address, and other personal information to create an account. This information is used for billing and account verification purposes.
- Set up payment details: You’ll need to provide your payment information, such as your credit card or PayPal account, to pay for your hosting plan.
File Transfer
Once you’ve created an account with a server host, you need to transfer your website files to the server. This can be done using a File Transfer Protocol (FTP) client or a web-based file manager.
- Use an FTP client: FTP clients are software applications that allow you to transfer files between your computer and a server. Popular FTP clients include FileZilla, Cyberduck, and WinSCP.
- Use a web-based file manager: Some server hosts offer web-based file managers that allow you to manage your files directly through your web browser. This is a convenient option if you don’t want to install an FTP client.
Server Configuration
Once your website files are on the server, you need to configure various settings to ensure optimal performance and security. This involves managing databases, setting up security protocols, and configuring email accounts.
Database Management
Many websites rely on databases to store and manage data, such as user information, product catalogs, and blog posts. Here’s how to manage databases on your server host:
- Create a database: Most server hosts provide tools for creating databases. You’ll need to choose a database name and specify the database type (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL).
- Configure database access: You’ll need to create a database user and grant them access to the database. This allows your website or application to connect to and interact with the database.
- Import data: Once your database is set up, you can import data from your local computer or other sources. This can be done using tools provided by your server host or by using a database management system (DBMS).
Security Protocols
Security is crucial for any website or application. Here are some security protocols you should configure on your server host:
- Enable SSL/TLS: SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) encrypts communication between your website and users’ web browsers. This protects sensitive information, such as credit card details, from being intercepted by unauthorized individuals. You can enable SSL/TLS through your server host’s control panel or by installing an SSL certificate on your server.
- Install a firewall: A firewall acts as a barrier between your server and the internet, blocking unauthorized access. Most server hosts provide firewalls as part of their hosting plans. You can also configure additional firewall rules to enhance security.
- Keep software updated: Regularly updating your server software, including the operating system and any applications, helps patch security vulnerabilities. This ensures your server is protected from the latest threats.
Email Accounts
Many websites use email accounts for communication with users, such as sending notifications, confirmations, and support inquiries. Here’s how to set up email accounts on your server host:
- Create email accounts: Most server hosts provide tools for creating email accounts. You’ll need to choose a username and password for each account.
- Configure email settings: You’ll need to configure email settings, such as the incoming and outgoing mail servers, to ensure emails can be sent and received correctly.
- Set up email forwarding: You can set up email forwarding to automatically redirect emails from one account to another. This can be useful for managing multiple email accounts or for sending emails from a different address.
Step-by-Step Guide for Server Host Configuration
Here’s a step-by-step guide for configuring your server host for optimal performance and security:
- Register a domain name: Choose a domain registrar and search for an available domain name that is relevant to your website or application. Register the domain name and pay the associated fees.
- Create an account with a server host: Select a server host that offers the features and pricing that best suit your needs. Create an account by providing personal information and setting up payment details.
- Transfer website files: Use an FTP client or a web-based file manager to transfer your website files to the server. Ensure all files are uploaded correctly and are accessible to your website or application.
- Configure databases: If your website or application uses a database, create a database and configure access for your website or application. Import data from your local computer or other sources.
- Enable SSL/TLS: Secure your website by enabling SSL/TLS. This ensures that communication between your website and users’ web browsers is encrypted.
- Install a firewall: Configure a firewall to block unauthorized access to your server. This helps protect your server from malicious attacks.
- Keep software updated: Regularly update your server software, including the operating system and any applications, to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Create email accounts: Set up email accounts for communication with users. Configure email settings and set up email forwarding if needed.
Server Host Security
In the digital realm, server hosts are the backbone of countless online services and applications. Ensuring their security is paramount, as vulnerabilities can expose sensitive data, disrupt operations, and lead to significant financial losses. A robust security strategy is essential to safeguard server hosts from various threats and ensure the integrity and availability of the services they support.
Common Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
Server hosts face a multitude of security threats, each posing unique challenges. Understanding these threats is crucial for implementing effective security measures.
- Malware: Malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware, can infiltrate server hosts, corrupt data, steal information, or disrupt operations. Malware can be spread through infected attachments, malicious websites, or vulnerabilities in software applications.
- DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm server hosts with a flood of traffic, rendering them unavailable to legitimate users. These attacks can cripple websites, online services, and critical infrastructure, causing significant downtime and financial losses.
- Unauthorized Access: Unsecured server hosts are vulnerable to unauthorized access, allowing attackers to steal data, modify system settings, or launch further attacks. Weak passwords, unpatched vulnerabilities, and misconfigured security settings can all contribute to unauthorized access.
Security Best Practices for Server Hosts
A comprehensive security strategy encompasses various best practices to mitigate risks and protect server hosts from threats.
- Firewall Configuration: Firewalls act as a barrier between the server host and the external network, blocking unauthorized access and malicious traffic. Configuring firewalls to allow only necessary traffic and block suspicious connections is crucial for security.
- Password Management: Strong passwords are essential to prevent unauthorized access. Employing a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, and regularly changing passwords can significantly enhance security. Additionally, using a password manager to store and manage passwords securely is recommended.
- Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits are essential to identify and address vulnerabilities. These audits involve scanning for known vulnerabilities, reviewing system logs, and assessing security configurations. Identifying and patching vulnerabilities promptly is crucial to prevent exploitation.
- Software Updates: Software vendors regularly release security updates to address vulnerabilities discovered in their products. Keeping software up to date ensures that server hosts are protected against the latest threats. Automating software updates can streamline the process and ensure timely patching.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data stored on server hosts protects it from unauthorized access, even if the server host is compromised. Encryption algorithms use mathematical formulas to scramble data, making it unreadable without the correct decryption key.
- Network Segmentation: Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments can limit the impact of security breaches. By separating sensitive systems and data from less critical ones, attackers are prevented from accessing critical resources if one segment is compromised.
- Security Monitoring and Logging: Implementing security monitoring tools and logging systems is essential for detecting suspicious activity and identifying potential threats. These tools can track network traffic, user activity, and system events, providing valuable insights for security analysis.
Server Host Scalability and Growth
As your website grows and attracts more visitors, it’s crucial to ensure your server host can handle the increased traffic and demand. Server host scalability refers to the ability of your hosting solution to adapt to changing needs and accommodate website growth without compromising performance.
Scalability Options
Choosing the right scalability options is essential for a smooth and seamless website growth experience. Here are some common approaches:
- Adding Resources: This involves increasing the available resources on your existing server, such as CPU power, RAM, or storage space. This can be done by upgrading your hosting plan or contacting your hosting provider to request additional resources.
- Upgrading Hosting Plans: As your website’s needs evolve, you may need to move to a higher-tier hosting plan. This often provides access to more powerful hardware, improved performance, and additional features.
- Migrating to a Different Hosting Provider: If your current hosting provider cannot meet your scaling requirements, migrating to a different provider with more robust scalability options might be necessary.
Best Practices for Managing Scalability
Proactive planning and management are essential for smooth website growth.
- Monitor Website Performance: Regularly track key metrics like website loading time, server response time, and resource utilization. This helps identify potential bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Plan for Future Growth: Anticipate future traffic increases and resource requirements. This allows you to choose a hosting solution with enough headroom to accommodate growth without encountering performance issues.
- Implement Caching Mechanisms: Caching helps reduce server load by storing frequently accessed content closer to users. This can significantly improve website performance and reduce the need for immediate scaling.
- Optimize Website Code and Content: Streamlining your website code and optimizing images and other media can reduce server load and improve performance, delaying the need for scaling.
- Consider Load Balancing: Load balancing distributes traffic across multiple servers, ensuring no single server is overloaded. This can be particularly helpful for high-traffic websites.
- Automate Scaling: Some hosting providers offer automated scaling solutions that automatically adjust resources based on real-time traffic patterns. This ensures your website remains responsive even during traffic surges.
Server Host Costs and Pricing

Choosing the right server host is crucial for your website or application’s success. However, alongside performance and features, cost is a significant factor to consider. Understanding server host pricing models and cost factors can help you make informed decisions and optimize your budget.
Pricing Models and Cost Factors
Server host pricing models vary depending on the type of hosting service you choose. Here are some common models and the factors that influence their costs:
- Shared Hosting: This is the most affordable option, where multiple websites share the same server resources. Costs are typically based on a monthly subscription fee and can range from a few dollars to tens of dollars per month. Factors influencing shared hosting costs include:
- Storage Space: The amount of disk space allocated to your website.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data transfer allowed for your website’s traffic.
- Number of Websites: Some shared hosting plans allow you to host multiple websites on the same account.
- Features: Additional features like email accounts, databases, and security measures can affect pricing.
- VPS Hosting: Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting provides a dedicated portion of a physical server, offering more resources and control than shared hosting. VPS pricing is usually based on a monthly subscription fee and can range from tens to hundreds of dollars per month. Cost factors include:
- CPU Cores and RAM: The amount of processing power and memory allocated to your VPS.
- Storage Space: The amount of disk space available for your website files and databases.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data transfer allowed for your website’s traffic.
- Operating System: The operating system you choose for your VPS can affect pricing.
- Dedicated Server Hosting: Dedicated server hosting provides you with an entire physical server dedicated solely to your website or application. This offers the highest level of resources and control. Dedicated server pricing is typically based on a monthly subscription fee and can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars per month. Cost factors include:
- Server Specifications: The type of server (e.g., CPU, RAM, storage), its configuration, and its location all influence pricing.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data transfer allowed for your website’s traffic.
- Management Services: Some providers offer managed dedicated server hosting, which includes server administration and maintenance, adding to the cost.
- Cloud Hosting: Cloud hosting utilizes a network of servers to distribute your website’s workload. Pricing is typically based on a pay-as-you-go model, where you pay only for the resources you use. Cloud hosting costs can vary significantly depending on your usage and the provider’s pricing structure. Cost factors include:
- Compute Resources: The amount of CPU and RAM you need for your website or application.
- Storage Space: The amount of disk space required for your website files and databases.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data transfer allowed for your website’s traffic.
- Traffic and Usage: Cloud hosting pricing often scales with your website’s traffic and resource usage.
Comparative Analysis of Server Host Providers
Several server host providers offer a wide range of hosting plans and pricing options. Here’s a comparative analysis of some popular providers and their pricing plans:
- GoDaddy: GoDaddy is a well-known provider offering a variety of hosting plans, including shared, VPS, and dedicated servers. Their pricing is competitive, starting from a few dollars per month for shared hosting and ranging up to hundreds of dollars for dedicated servers.
- Bluehost: Bluehost is another popular provider known for its reliable hosting services. Their pricing is similar to GoDaddy, with shared hosting plans starting from a few dollars per month and dedicated server plans costing hundreds of dollars per month.
- HostGator: HostGator is a reputable provider offering a wide range of hosting plans, including shared, VPS, dedicated servers, and cloud hosting. Their pricing is competitive, with shared hosting plans starting from a few dollars per month and dedicated server plans costing hundreds of dollars per month.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is a leading cloud hosting provider offering a vast array of services and pricing options. Their pay-as-you-go pricing model allows you to pay only for the resources you use, making it a cost-effective option for businesses with fluctuating workloads.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP is another major cloud hosting provider offering a wide range of services and pricing options. Their pay-as-you-go pricing model is similar to AWS, allowing you to pay only for the resources you use.
Factors Influencing Server Host Costs
Several factors can influence server host costs, besides the pricing models discussed above. These factors can affect your overall hosting expenses:
- Storage Space: The amount of disk space you need for your website files, databases, and other data. More storage space typically means higher costs.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data transfer allowed for your website’s traffic. Higher bandwidth allows for more traffic and can increase costs.
- Technical Support: The level of technical support provided by your server host. Some providers offer 24/7 support, while others have limited support hours. Higher levels of support typically come at a higher cost.
- Features: Additional features offered by your server host, such as email accounts, databases, security measures, and website builder tools, can affect pricing.
- Location: The physical location of your server can influence costs. Servers located in certain regions may have higher costs due to factors like data center infrastructure and local regulations.
- Contract Length: Some server hosts offer discounts for longer-term contracts.
Server Host Use Cases and Applications
Server hosting plays a crucial role in enabling various online functionalities, ranging from simple websites to complex applications. Understanding the diverse use cases and applications of server hosts is essential for choosing the right hosting solution for your specific needs.
Hosting Websites
Websites are the most common application of server hosts. They provide a platform for businesses and individuals to showcase their content, products, or services to a global audience. The requirements for hosting a website depend on factors such as traffic volume, content type, and desired performance. For instance, a simple blog website might be adequately hosted on a shared hosting plan, while a high-traffic e-commerce website would require a dedicated server or cloud hosting solution.
Hosting Web Applications
Web applications are software programs that run on a server and are accessed through a web browser. Examples include online shopping carts, social media platforms, and content management systems (CMS). Hosting web applications requires specialized server configurations and resources to ensure optimal performance and scalability.
Hosting Databases
Databases are essential for storing and managing large amounts of data. Server hosts provide the infrastructure for hosting databases, which are used by websites, applications, and other systems. The type of database server required depends on the size and complexity of the data, the number of users, and the performance requirements.
Hosting Email Servers
Email servers are responsible for sending and receiving emails. Server hosts can be configured to act as email servers, providing secure and reliable email services. Businesses and individuals can choose from various email hosting solutions, such as shared email hosting, dedicated email servers, and cloud-based email services.
Hosting Gaming Servers, Server host
Gaming servers provide the infrastructure for online multiplayer games. Server hosts are used to host game servers, allowing players from around the world to connect and play together. The requirements for hosting gaming servers depend on the game, the number of players, and the desired performance.
Hosting Other Applications
Server hosts can be used to host a wide range of other applications, including:
- File sharing services: Server hosts can be used to create file sharing platforms, allowing users to store and share files online.
- Streaming services: Server hosts are essential for streaming services, such as video-on-demand platforms and live streaming services.
- Virtual private servers (VPS): Server hosts can be used to create virtual private servers, providing a dedicated environment for running applications.
- Cloud computing platforms: Server hosts are a fundamental component of cloud computing platforms, providing the infrastructure for running applications and services in the cloud.
Examples of Successful Implementations
* Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading cloud computing platform that utilizes server hosts to provide a wide range of services, including web hosting, database hosting, and application hosting. AWS powers many popular websites and applications, including Netflix, Airbnb, and Pinterest.
* Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is another major cloud computing platform that relies on server hosts to deliver services like web hosting, database hosting, and machine learning. GCP is used by companies like Spotify, Snapchat, and The New York Times.
* Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing platform that provides server hosting services for businesses of all sizes. Azure powers applications for companies like Ford, Starbucks, and General Electric.
Server Host Comparison and Recommendations

Choosing the right server host can be a daunting task, as there are many providers available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. To help you make an informed decision, this section will provide a comparison of popular server host providers based on key factors such as pricing, features, performance, and customer support. It will also offer recommendations for specific server host providers based on different needs and requirements.
Server Host Provider Comparison
This table compares popular server host providers based on key factors:
| Provider | Pricing | Features | Performance | Customer Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GoDaddy | Starts at $5.99/month | Shared hosting, VPS hosting, dedicated servers, domain registration, SSL certificates | Average performance | 24/7 customer support via phone, email, and chat |
| Bluehost | Starts at $2.95/month | Shared hosting, VPS hosting, dedicated servers, WordPress hosting, domain registration, SSL certificates | Good performance | 24/7 customer support via phone, email, and chat |
| HostGator | Starts at $2.75/month | Shared hosting, VPS hosting, dedicated servers, WordPress hosting, domain registration, SSL certificates | Good performance | 24/7 customer support via phone, email, and chat |
| SiteGround | Starts at $3.95/month | Shared hosting, VPS hosting, dedicated servers, WordPress hosting, domain registration, SSL certificates | Excellent performance | 24/7 customer support via phone, email, and chat |
| DreamHost | Starts at $2.59/month | Shared hosting, VPS hosting, dedicated servers, WordPress hosting, domain registration, SSL certificates | Good performance | 24/7 customer support via email and chat |
Server Host Recommendations
The best server host for you will depend on your specific needs and requirements. Here are some recommendations:
- For small businesses and personal websites: GoDaddy, Bluehost, and HostGator are all good options for shared hosting. They offer affordable pricing and a wide range of features.
- For businesses with high traffic websites: SiteGround and DreamHost are good options for VPS hosting and dedicated servers. They offer better performance and scalability than shared hosting.
- For WordPress websites: Bluehost, HostGator, and SiteGround are all excellent choices for WordPress hosting. They offer optimized performance and features specifically for WordPress websites.
- For businesses with specific needs: There are many other server host providers that specialize in specific areas, such as e-commerce, gaming, and cloud hosting. It’s important to research and compare providers to find the best fit for your needs.
Conclusive Thoughts
As we conclude our exploration of server hosts, it’s clear that choosing the right hosting solution is a fundamental step towards a successful online presence. By understanding the diverse options available, the factors to consider, and the best practices for setup, management, and optimization, you can build a robust and reliable foundation for your website or application. With the right server host, your digital dreams can soar to new heights.
A server host provides the infrastructure for your website or application to run smoothly. But sometimes, you might want to get your hands dirty and personalize your setup. If you’re feeling adventurous, you can explore the world of diy web hosting, where you can customize every aspect of your server environment.
This gives you greater control and flexibility, but it also requires a deeper understanding of server administration.