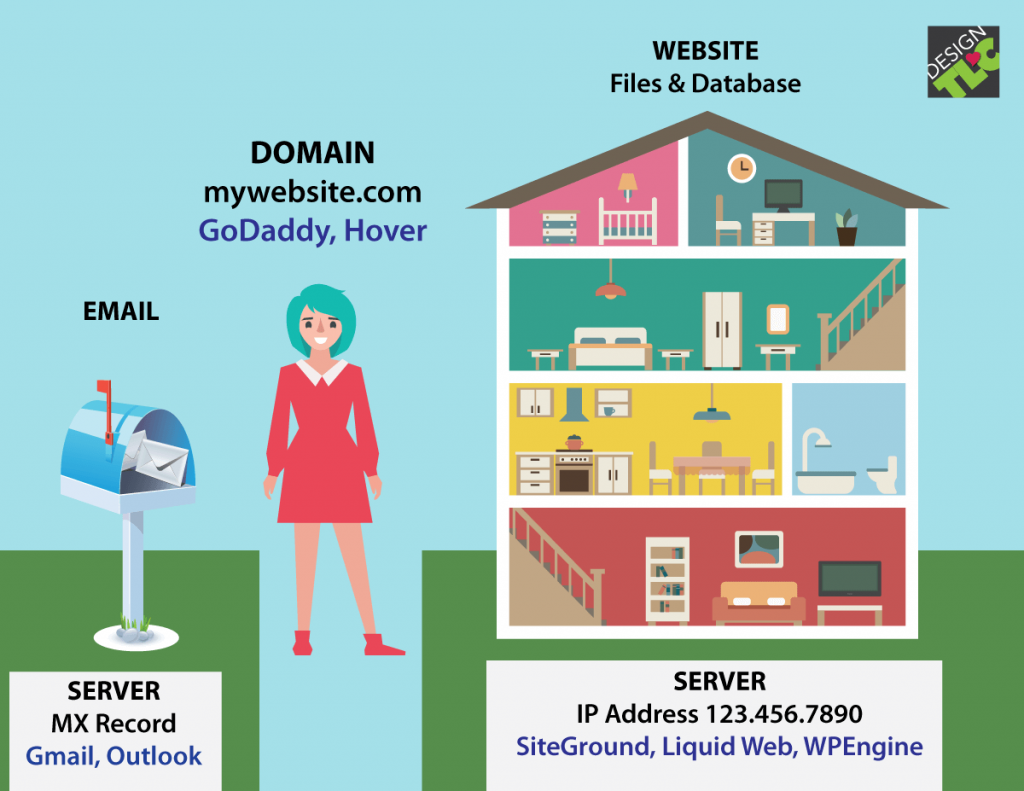
Hostings are the foundation of any website, providing the digital space where your online presence comes to life. From humble beginnings to complex online empires, understanding the different types of hosting and their nuances is crucial for achieving your website goals. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or a budding entrepreneur, this comprehensive guide delves into the world of hostings, offering insights into choosing the right plan, optimizing performance, and ensuring security for your digital assets.
This guide explores the diverse landscape of hosting options, encompassing shared, VPS, dedicated, and cloud hosting. It unravels the key features that distinguish one hosting provider from another, empowering you to make informed decisions. Additionally, we’ll navigate the intricacies of website migration, optimization, and security, equipping you with the knowledge to maintain a thriving online presence.
Essential Hosting Features
Choosing the right hosting provider is crucial for any website, regardless of its size or purpose. A reliable hosting provider ensures your website is accessible to visitors, performs well, and remains secure. Here are some key features to consider when evaluating hosting options.
Uptime
Uptime refers to the percentage of time a website is accessible to visitors. High uptime is essential for any website, as downtime can lead to lost visitors, potential customers, and damage to your reputation. A reliable hosting provider will offer an uptime guarantee of at least 99.9%, which means your website will be unavailable for less than 43 minutes per month.
An uptime guarantee is a commitment from the hosting provider to maintain a certain level of uptime for your website.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transferred between your website and visitors. It’s essential to choose a hosting plan with enough bandwidth to handle your website’s traffic volume. Websites with high traffic, such as e-commerce stores or popular blogs, require more bandwidth than websites with low traffic.
Storage
Storage refers to the amount of space available on the server to store your website’s files, including images, videos, and databases. The amount of storage you need depends on the size of your website and the type of content you host.
Websites with large amounts of multimedia content, such as video streaming platforms or online galleries, require more storage than websites with primarily text-based content.
Security
Security is a critical aspect of hosting, as it protects your website and your visitors from malicious attacks. Look for a hosting provider that offers robust security features, such as firewalls, malware protection, and regular security updates.
Customer Support
Customer support is essential for any hosting provider, as you may need assistance with technical issues or have questions about your hosting plan. Choose a provider that offers responsive and knowledgeable customer support, available via phone, email, or live chat.
SSL Certificates
SSL certificates are digital certificates that encrypt the communication between your website and visitors, ensuring the data exchanged is secure.
SSL certificates are essential for websites that handle sensitive information, such as credit card details or personal data.
SSL certificates are also important for search engine optimization (), as Google and other search engines prioritize websites with SSL certificates.
Website Backups, Hostings
Website backups are essential for protecting your website’s data from accidental deletion or data loss due to a security breach. A good hosting provider will offer regular website backups, allowing you to restore your website to a previous state if necessary.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
CDNs are networks of servers distributed around the world that deliver content to visitors from the server closest to their location. CDNs can improve website performance by reducing latency and improving loading times, especially for visitors located far from the primary server.
CDNs are particularly beneficial for websites with high traffic or global audiences.
Website Optimization

A website’s performance is crucial for user engagement and search engine ranking. A slow website can lead to frustrated visitors, higher bounce rates, and lower conversions. Optimizing your website for speed and performance is essential for a successful online presence.
Server Location
The physical location of your server can significantly impact website loading times. Choosing a server located close to your target audience can reduce latency and improve performance. For example, if your website targets users in North America, choosing a server in the United States will generally result in faster loading times for visitors in that region.
Caching
Caching is a technique that stores copies of frequently accessed website data, such as images, HTML files, and CSS stylesheets, on a server. When a visitor requests a page, the server can serve the cached version instead of processing the request from scratch. This significantly reduces loading times and improves performance.
Image Optimization
Images are often the largest files on a website, and they can significantly impact loading times. Optimizing images for size and format can improve website performance. This includes using image compression tools, choosing the right image format (JPEG, PNG, WebP), and using responsive images that adjust to different screen sizes.
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN is a network of servers distributed globally. When a visitor requests a website, the CDN delivers the content from the server closest to the visitor. This reduces latency and improves loading times, especially for users located far from the website’s main server.
Website Structure and Code
A well-structured website with clean and optimized code can significantly improve performance. This includes minimizing HTTP requests, using efficient CSS and JavaScript, and reducing the number of external scripts.
Future Trends in Hosting

The hosting landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing user demands. Emerging trends like serverless computing and edge computing are reshaping how websites are built, deployed, and managed. Understanding these trends is crucial for website owners and businesses seeking to optimize performance, scalability, and security.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is a cloud-based execution environment where developers can run code without managing servers. It allows for greater flexibility and scalability, as resources are automatically provisioned and scaled based on demand. This eliminates the need for server administration, allowing developers to focus on building applications.
Benefits of Serverless Computing
- Reduced Infrastructure Costs: Serverless computing eliminates the need to invest in and maintain physical or virtual servers, significantly reducing infrastructure costs.
- Increased Scalability: Resources are automatically scaled up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during traffic spikes.
- Enhanced Developer Productivity: Developers can focus on building applications without worrying about server management, leading to faster development cycles.
- Improved Security: Cloud providers handle server security, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities and attacks.
Examples of Serverless Computing Platforms
- AWS Lambda: A serverless compute service offered by Amazon Web Services.
- Google Cloud Functions: A serverless platform provided by Google Cloud Platform.
- Azure Functions: A serverless compute service offered by Microsoft Azure.
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to users, reducing latency and improving performance. This approach distributes processing power to edge locations, such as data centers, cell towers, and even user devices.
Benefits of Edge Computing
- Reduced Latency: By processing data closer to users, edge computing minimizes network delays and improves responsiveness.
- Enhanced Performance: Faster data processing and reduced latency result in a smoother user experience, particularly for real-time applications.
- Improved Scalability: Distributing processing power across edge locations enhances scalability, allowing for handling increased traffic and demand.
- Increased Security: Edge computing can enhance security by isolating sensitive data and processing it closer to users, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Examples of Edge Computing Applications
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs use edge servers to deliver content closer to users, improving website performance and reducing latency.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Edge computing is essential for processing data from IoT devices in real-time, enabling applications like smart homes and industrial automation.
- Gaming and Streaming: Edge computing reduces latency in gaming and streaming applications, providing a smoother and more immersive experience.
Conclusive Thoughts: Hostings

In conclusion, understanding hostings is paramount to building a successful website. By navigating the various hosting types, considering essential features, and prioritizing security, you can establish a solid foundation for your online endeavors. As the digital landscape evolves, staying abreast of emerging trends and adapting your hosting strategy ensures a seamless and prosperous online journey.