Cloud hosting has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals manage their online presence. It offers a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution for hosting websites, applications, and data. By leveraging the power of remote servers and data centers, cloud hosting eliminates the need for physical infrastructure, allowing users to access resources on demand.
Cloud hosting encompasses a wide range of services, each tailored to specific needs and use cases. From Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) to Software as a Service (SaaS), different cloud hosting models cater to various requirements, providing a spectrum of options for businesses of all sizes.
What is Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting is a way of storing and accessing data and applications over the internet, instead of on your own physical servers. Think of it like renting space on a massive, shared computer network, rather than owning and maintaining your own.
Cloud hosting relies on a network of data centers around the world, with powerful servers and advanced infrastructure. This allows you to access your data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, without needing to worry about hardware, software updates, or security.
Examples of Cloud Hosting Services
Several major players dominate the cloud hosting market, offering a wide range of services and features.
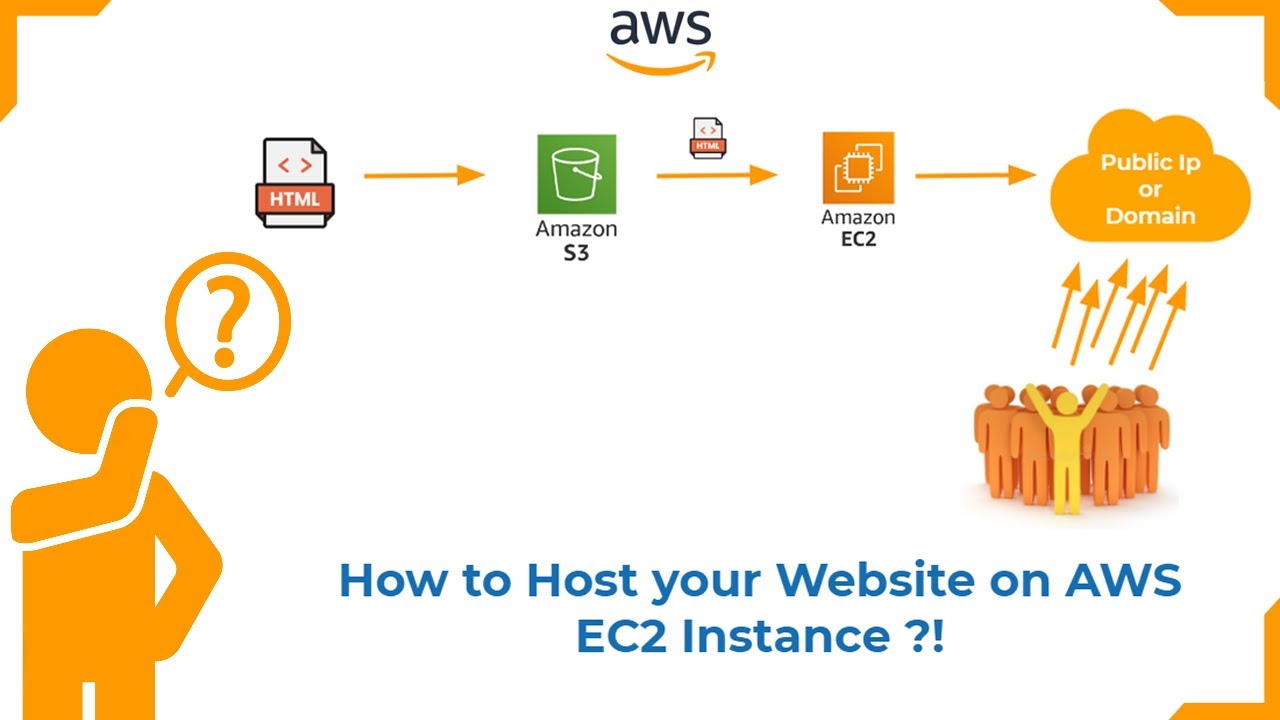
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): One of the largest and most comprehensive cloud platforms, offering a vast array of services, including computing, storage, networking, databases, and more.
- Microsoft Azure: Microsoft’s cloud platform, known for its integration with Microsoft technologies and its enterprise-grade security features.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Google’s cloud platform, known for its AI and machine learning capabilities, as well as its focus on data analytics.
Advantages of Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting offers numerous advantages over traditional hosting, making it a popular choice for businesses and individuals alike. These benefits include scalability, cost-effectiveness, enhanced security, and improved accessibility.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud hosting provides a high level of scalability and flexibility, allowing you to easily adjust your resources as your needs change. This is because cloud resources are virtualized, meaning they can be dynamically allocated and re-allocated on demand. For instance, if your website experiences a sudden surge in traffic, cloud hosting can automatically scale up to accommodate the increased load, ensuring a smooth user experience. Conversely, if your traffic decreases, you can scale down your resources to reduce costs. This dynamic nature of cloud hosting allows you to pay only for the resources you use, making it a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes.
Cost-Effectiveness and Pay-as-You-Go Models
Cloud hosting offers a pay-as-you-go model, where you pay only for the resources you use. This eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and software, making it a cost-effective solution, especially for startups and small businesses. Moreover, cloud providers often offer various pricing plans, allowing you to choose the option that best suits your budget and needs.
Enhanced Security and Data Redundancy
Cloud hosting providers invest heavily in security measures to protect your data from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and other threats. They typically employ advanced security technologies, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption. Additionally, cloud hosting offers data redundancy, ensuring that your data is backed up and stored in multiple locations. This redundancy safeguards your data from data loss in case of hardware failure or natural disasters.
Improved Accessibility and Remote Management
Cloud hosting enables you to access your website and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility is crucial for businesses with remote teams or those needing to manage their website or applications on the go. Furthermore, cloud hosting allows you to manage your resources remotely, simplifying server administration and reducing the need for on-site IT personnel.
Types of Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is available in various models, each catering to specific needs and offering distinct features. Understanding these models is crucial for selecting the right cloud solution for your business.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS providers offer access to fundamental computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, on a pay-as-you-go basis. This model provides the most flexibility and control, allowing users to manage their infrastructure like virtualized hardware.
- Characteristics: Users have complete control over the operating system, applications, and software installed on their virtual machines.
- Use Cases: IaaS is ideal for businesses requiring high levels of customization and flexibility, such as running complex applications, deploying large-scale infrastructure, and managing mission-critical workloads.
- Examples: Popular IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Platform as a Service (PaaS), Cloud hosting
PaaS providers abstract away the underlying infrastructure, offering a platform for developing and deploying applications without managing servers or operating systems. This model focuses on simplifying the development and deployment process, allowing developers to concentrate on application logic.
- Characteristics: PaaS providers manage the infrastructure, operating system, middleware, and runtime environment, allowing developers to focus on application development and deployment.
- Use Cases: PaaS is suitable for businesses that need to rapidly develop and deploy applications, such as web applications, mobile applications, and data analytics platforms.
- Examples: Popular PaaS providers include Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Google App Engine.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS providers offer fully managed applications accessible through a web browser or mobile app. This model eliminates the need for users to install, manage, or update software, making it a convenient and cost-effective solution.
- Characteristics: SaaS applications are hosted and managed by the provider, with users accessing them through a web browser or mobile app. Users do not need to install or manage software.
- Use Cases: SaaS is ideal for businesses that need to access applications quickly and easily, such as email, CRM, project management, and accounting software.
- Examples: Popular SaaS providers include Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, and Google Workspace.
Key Considerations for Choosing Cloud Hosting
Choosing the right cloud hosting provider is crucial for ensuring your website or application runs smoothly and effectively. There are several key factors to consider, which will directly impact your overall experience.
Performance Metrics
Performance metrics are crucial for evaluating the quality and reliability of a cloud hosting provider. They provide insights into how your website or application will perform in real-world scenarios.
- Uptime: This metric represents the percentage of time your website or application is accessible to users. High uptime is essential for maintaining user satisfaction and avoiding revenue loss. Aim for providers with an uptime guarantee of 99.9% or higher.
- Latency: This refers to the time it takes for data to travel between your server and users. Lower latency translates to faster loading times and a more responsive user experience. Consider providers with servers located geographically close to your target audience to minimize latency.
- Bandwidth: This represents the amount of data that can be transferred between your server and users in a given time period. Sufficient bandwidth is essential for handling traffic spikes and ensuring your website or application remains accessible even during peak hours. Choose a provider offering scalable bandwidth options to accommodate your needs.
Security Features
Cloud hosting providers offer various security features to protect your data and applications from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Data Encryption: This involves converting your data into an unreadable format, making it inaccessible to unauthorized parties. Look for providers that offer data encryption both at rest (when stored on servers) and in transit (while being transferred).
- Firewalls: These act as barriers between your server and the internet, blocking unauthorized access attempts. Ensure the provider offers robust firewall protection, including intrusion detection and prevention systems.
- Regular Security Updates: Cloud providers should regularly update their systems and software to patch vulnerabilities and mitigate potential security risks. Choose providers with a proven track record of implementing security updates promptly.
- Compliance Standards: Depending on your industry or the nature of your data, you may need to comply with specific security standards. For example, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for healthcare data or the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for handling credit card information. Verify that the provider meets the relevant compliance standards for your needs.
Pricing Models and Support Options
Cloud hosting providers offer different pricing models and support options to suit various budgets and requirements.
- Pricing Models: Common pricing models include pay-as-you-go, where you pay only for the resources you use, and fixed monthly fees for a predetermined package of resources. Evaluate the pricing models offered by different providers and choose one that aligns with your budget and expected usage patterns.
- Support Options: Cloud providers offer varying levels of support, from basic email or chat support to dedicated account managers and 24/7 phone support. Assess your support needs and choose a provider that offers the appropriate level of assistance.
Cloud Hosting for Different Use Cases
Cloud hosting is a versatile solution that caters to a wide range of use cases, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. It provides a robust infrastructure for websites, applications, data storage, and more, making it an ideal choice for businesses and individuals alike.
Websites and Applications
Cloud hosting provides the necessary infrastructure to host websites and applications, allowing them to be accessible online. It offers a range of services, including:
- Web servers: Cloud providers offer virtual servers that can host websites and applications, ensuring they are available and performant.
- Databases: Cloud hosting includes databases that store and manage website and application data, ensuring data integrity and accessibility.
- Load balancing: This distributes traffic across multiple servers, ensuring website and application performance even during peak traffic periods.
- Content delivery networks (CDNs): CDNs deliver website content from geographically distributed servers, improving website speed and performance for users worldwide.
By leveraging cloud hosting, businesses can ensure their websites and applications are reliable, scalable, and secure.
Data Storage and Backup
Cloud hosting provides a secure and scalable solution for data storage and backup.
- Cloud storage: Cloud providers offer various storage options, including object storage, block storage, and file storage, allowing businesses to store data of different types and sizes.
- Data backup: Cloud hosting simplifies data backup by providing automated backup solutions that regularly back up data to the cloud. This ensures data protection in case of hardware failures or other disasters.
- Disaster recovery: Cloud hosting enables businesses to quickly recover data and applications in the event of a disaster, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
Cloud hosting provides a comprehensive data management solution, ensuring data security, availability, and accessibility.
E-commerce Platforms
Cloud hosting is a popular choice for e-commerce platforms due to its scalability, security, and reliability.
- Scalability: Cloud hosting allows e-commerce platforms to easily scale their resources based on traffic fluctuations, ensuring a seamless customer experience even during peak shopping seasons.
- Security: Cloud hosting providers offer robust security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption, protecting sensitive customer data and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
- Payment processing: Cloud hosting integrates seamlessly with payment gateways, enabling secure and reliable online payment processing.
By leveraging cloud hosting, e-commerce businesses can create secure, scalable, and reliable online stores that meet the needs of their customers.
Software Development and Deployment
Cloud hosting is a valuable tool for software development and deployment, providing a flexible and efficient platform for building and delivering applications.
- Development environments: Cloud hosting provides developers with virtual machines and other resources needed to build and test applications, enabling rapid development cycles.
- Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD): Cloud hosting supports CI/CD pipelines, automating the build, test, and deployment process, accelerating software delivery and improving code quality.
- Microservices architecture: Cloud hosting facilitates the development and deployment of microservices, enabling businesses to build complex applications by breaking them down into smaller, independent services.
Cloud hosting empowers software development teams to build, test, and deploy applications quickly and efficiently, accelerating innovation and delivering value to users.
Cloud Hosting and Security
Cloud hosting, while offering numerous advantages, also introduces new security considerations. It’s crucial to understand the potential threats and implement robust security measures to protect your data and applications.
Security Threats in the Cloud
Cloud environments are not immune to security threats. In fact, the distributed nature of cloud infrastructure can make it more challenging to secure. Here are some common security threats:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data stored in the cloud is a significant concern. This can occur through various means, such as exploiting vulnerabilities in cloud services or gaining access to user credentials.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: These attacks aim to disrupt the availability of cloud services by overwhelming them with traffic. This can impact application performance and user access.
- Malware and Viruses: Malicious software can infiltrate cloud environments and compromise data or systems. This can be done through phishing attacks, infected attachments, or vulnerabilities in cloud applications.
- Misconfigurations: Incorrectly configured cloud services or applications can create security loopholes. For example, misconfigured firewalls or storage access permissions can expose data to unauthorized access.
- Insider Threats: Employees with access to sensitive cloud data can pose a risk. This can include intentional or unintentional actions that compromise security.
Best Practices for Securing Cloud Infrastructure
To mitigate security threats in the cloud, it’s essential to implement robust security measures. Here are some best practices:
- Use Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication: Implement strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication for all user accounts. This adds an extra layer of security and makes it harder for unauthorized users to gain access.
- Implement a Comprehensive Security Policy: Establish clear security policies and procedures for managing cloud resources. This should cover access control, data encryption, incident response, and other critical security aspects.
- Regularly Patch and Update Systems: Keep all cloud services and applications up-to-date with the latest security patches. This helps to address vulnerabilities and mitigate the risk of exploits.
- Monitor Cloud Infrastructure: Use security monitoring tools to continuously monitor cloud environments for suspicious activity. This allows for early detection and response to security incidents.
- Leverage Cloud Security Services: Take advantage of cloud security services offered by providers. These services can help with vulnerability scanning, threat detection, and incident response.
Security Measures in Cloud Hosting
Here are some examples of security measures commonly used in cloud hosting:
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between the cloud infrastructure and the outside world, filtering traffic and blocking unauthorized access. They can be implemented at different levels, including network firewalls, application firewalls, and web application firewalls.
- Encryption: Data encryption is essential for protecting sensitive information in transit and at rest. Cloud providers typically offer encryption services, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) for data in transit and encryption at rest for data stored on their servers.
- Access Control: Access control mechanisms restrict user access to cloud resources based on roles and permissions. This ensures that only authorized individuals have access to specific data or applications.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Regular vulnerability scanning helps identify security weaknesses in cloud infrastructure and applications. This allows for timely patching and remediation.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can block or alert on potential security threats.
Cloud Hosting and Disaster Recovery
Cloud hosting plays a crucial role in disaster recovery planning, enabling businesses to minimize downtime and data loss in the face of unforeseen events.
Data Replication and Backup Strategies
Data replication and backup strategies are fundamental to ensuring business continuity in the event of a disaster. Cloud hosting providers offer various solutions to safeguard data:
- Data Replication: Cloud platforms replicate data across multiple data centers, ensuring that even if one center experiences an outage, copies of the data are available in other locations. This redundancy provides high availability and minimizes downtime.
- Regular Backups: Cloud providers automatically back up data at regular intervals, allowing businesses to restore data to a specific point in time if needed. This ensures that data is not lost even if the primary data source is compromised.
- Off-site Backup: Cloud hosting allows businesses to store backups off-site, further reducing the risk of data loss due to local disasters or physical damage to the primary data center.
Business Continuity
Cloud hosting facilitates business continuity by providing a platform for businesses to continue operating even during disruptions.
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS): Cloud providers offer DRaaS solutions that automate the recovery process in the event of a disaster. These solutions can quickly provision virtual machines, databases, and other resources in a different data center, allowing businesses to resume operations with minimal downtime.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud hosting provides scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to quickly adjust resources based on their needs during a disaster recovery event. This ensures that they have the necessary capacity to handle increased demand or to switch to alternative systems.
- Reduced Costs: Cloud hosting can reduce the cost of disaster recovery planning compared to traditional on-premises solutions. Businesses can avoid the expense of maintaining dedicated disaster recovery infrastructure and can pay only for the resources they use.
Cloud Hosting and Future Trends
Cloud hosting has undergone a remarkable evolution, transitioning from a niche technology to an indispensable component of modern computing. As we move forward, the cloud is poised to become even more integrated into our lives, driven by emerging trends that are reshaping the landscape of computing.
The Evolution of Cloud Hosting Technologies
The journey of cloud hosting has been marked by significant advancements in technology and infrastructure. Early cloud services were primarily focused on providing basic storage and computing resources, often delivered through virtualized servers. However, the evolution of cloud computing has led to the development of sophisticated platforms that offer a wide range of services, including:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This foundational layer provides virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, allowing users to build and deploy their own applications. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS platforms offer a more comprehensive environment for application development and deployment, providing tools, frameworks, and services that simplify the process. Popular PaaS options include Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Google App Engine.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS applications are delivered over the internet, allowing users to access and use software without the need for installation or maintenance. Examples include Salesforce, Dropbox, and Google Workspace.
These advancements have made cloud hosting accessible to a broader range of users, enabling businesses of all sizes to leverage the benefits of cloud computing.
The Impact of Edge Computing and Serverless Computing
Emerging trends like edge computing and serverless computing are further driving the evolution of cloud hosting.
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the users, reducing latency and improving performance. This is particularly beneficial for applications that require real-time processing or low latency, such as streaming services, gaming, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Edge computing can be seen as an extension of cloud computing, pushing processing power to the edge of the network.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing allows developers to run code without managing servers. This approach eliminates the need for server provisioning, scaling, and maintenance, enabling developers to focus on building applications. Popular serverless platforms include AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, and Azure Functions.
Predictions About the Future of Cloud Hosting
The future of cloud hosting is bright, with several key trends shaping the landscape:
- Increased adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud strategies: Businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid cloud and multi-cloud strategies, leveraging the strengths of different cloud providers to meet their specific needs. This approach provides greater flexibility, resilience, and cost optimization.
- Growth of edge computing: Edge computing is expected to see significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for real-time data processing and low latency applications. This trend will further blur the lines between cloud computing and edge computing, creating a more distributed and interconnected computing environment.
- Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML): AI and ML are transforming cloud hosting by enabling intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and personalized experiences. Cloud providers are incorporating AI and ML into their platforms to optimize resource allocation, improve security, and enhance user experience.
- Focus on sustainability: Cloud providers are increasingly focusing on sustainability, implementing measures to reduce their environmental impact. This includes using renewable energy sources, optimizing resource utilization, and promoting energy-efficient practices.
As these trends continue to evolve, cloud hosting will become even more pervasive and integrated into our lives, empowering businesses and individuals to achieve their goals in a connected and dynamic world.
Real-World Examples of Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting has become increasingly popular in recent years, and for good reason. It offers numerous benefits over traditional hosting, such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. To better understand the real-world impact of cloud hosting, let’s explore some case studies of companies that have successfully implemented cloud solutions.
Netflix’s Transition to the Cloud
Netflix, a global streaming giant, was an early adopter of cloud computing. They recognized the need for a scalable and flexible infrastructure to handle the ever-increasing demand for their streaming services. In 2008, Netflix began migrating its infrastructure to Amazon Web Services (AWS), a move that proved to be transformative. By leveraging AWS’s vast computing power and global network, Netflix could quickly scale its services to meet peak demand during popular show launches and holiday seasons. This move allowed Netflix to deliver a seamless streaming experience to millions of users worldwide, even during periods of high traffic.
“Our cloud migration was a huge success. We were able to scale our infrastructure quickly and efficiently, and we’ve seen significant cost savings.” – Netflix CTO, Mike Kail
Comparing Cloud Hosting Providers
Choosing the right cloud hosting provider is crucial for your website’s performance, reliability, and scalability. With numerous providers offering a wide range of services and features, it can be challenging to determine the best fit for your specific needs. To simplify this process, this section will compare key features and pricing of popular cloud hosting providers, allowing you to make an informed decision.
Comparing Key Features and Pricing
A comprehensive comparison of cloud hosting providers involves evaluating various factors, including features, pricing, performance, security, customer support, and scalability. This table provides a high-level overview of key features and pricing for some popular cloud hosting providers.
| Provider | Key Features | Pricing | Pros and Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Wide range of services, including EC2, S3, Lambda, and more. Global infrastructure, high availability, and scalability. | Pay-as-you-go pricing model. Costs vary based on resource usage. |
|
| Microsoft Azure | Comprehensive cloud platform with services like Azure VMs, Azure SQL Database, and Azure App Service. Hybrid cloud capabilities and integration with Microsoft products. | Pay-as-you-go pricing model with various subscription options. |
|
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Offers a wide array of services, including Compute Engine, Cloud Storage, and BigQuery. Known for its AI and machine learning capabilities. | Pay-as-you-go pricing model with flexible options. |
|
| DigitalOcean | Offers a range of cloud services, including virtual machines, managed databases, and object storage. Known for its user-friendly interface and affordable pricing. | Fixed monthly pricing for virtual machines and other services. |
|
| Linode | Offers a range of cloud services, including virtual machines, managed databases, and object storage. Known for its reliable performance and competitive pricing. | Fixed monthly pricing for virtual machines and other services. |
|
Cloud Hosting Resources
This section provides a comprehensive list of valuable resources for delving deeper into the world of cloud hosting. Whether you’re a beginner seeking a foundational understanding or an experienced professional looking for advanced insights, these resources offer a wealth of information and guidance.
Websites and Documentation
These websites offer a wide range of information on cloud hosting, from introductory guides to technical documentation.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is a leading cloud platform offering a vast array of services, including compute, storage, networking, databases, and more. Their website provides extensive documentation, tutorials, and community forums. [Link: https://aws.amazon.com/](https://aws.amazon.com/)
- Microsoft Azure: Azure is another major cloud provider offering a comprehensive suite of services. Their website features documentation, tutorials, and resources for developers and businesses. [Link: https://azure.microsoft.com/](https://azure.microsoft.com/)
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP is a cloud platform known for its innovative services and robust infrastructure. Their website provides extensive documentation, tutorials, and community forums. [Link: https://cloud.google.com/](https://cloud.google.com/)
- DigitalOcean: DigitalOcean is a popular cloud provider known for its simplicity and ease of use. Their website offers tutorials, documentation, and community support. [Link: https://www.digitalocean.com/](https://www.digitalocean.com/)
- Linode: Linode is a cloud provider offering a range of virtual machines, storage, and networking services. Their website provides documentation, tutorials, and community forums. [Link: https://www.linode.com/](https://www.linode.com/)
- Cloud Foundry: Cloud Foundry is an open-source platform-as-a-service (PaaS) that simplifies application deployment and management. Their website provides documentation, tutorials, and community support. [Link: https://www.cloudfoundry.org/](https://www.cloudfoundry.org/)
- OpenStack: OpenStack is an open-source cloud operating system that provides a comprehensive platform for managing cloud infrastructure. Their website offers documentation, tutorials, and community resources. [Link: https://www.openstack.org/](https://www.openstack.org/)
Articles and Blog Posts
These articles and blog posts provide valuable insights and analysis on cloud hosting trends, best practices, and emerging technologies.
- Cloud Computing: A Beginner’s Guide (TechTarget): This comprehensive guide provides an overview of cloud computing, its different types, and its benefits. [Link: https://www.techtarget.com/searchcloudcomputing/definition/cloud-computing](https://www.techtarget.com/searchcloudcomputing/definition/cloud-computing)
- The Ultimate Guide to Cloud Hosting (Hostinger): This guide covers various aspects of cloud hosting, including its types, advantages, and considerations for choosing a provider. [Link: https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/cloud-hosting](https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/cloud-hosting)
- Cloud Hosting vs. Shared Hosting: Which is Right for You? (Namecheap): This article compares cloud hosting and shared hosting, highlighting their key differences and helping you determine the best option for your needs. [Link: https://www.namecheap.com/support/knowledgebase/cloud-hosting-vs-shared-hosting/](https://www.namecheap.com/support/knowledgebase/cloud-hosting-vs-shared-hosting/)
- Cloud Hosting Security: Best Practices and Tips (Cloudflare): This article discusses important security considerations for cloud hosting, including best practices and tips for protecting your data and applications. [Link: https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cloud/cloud-hosting-security/](https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cloud/cloud-hosting-security/)
- The Future of Cloud Hosting: Trends and Predictions (ZDNet): This article explores emerging trends and predictions for the future of cloud hosting, including the rise of edge computing, serverless computing, and artificial intelligence. [Link: https://www.zdnet.com/article/the-future-of-cloud-hosting-trends-and-predictions/](https://www.zdnet.com/article/the-future-of-cloud-hosting-trends-and-predictions/)
Books and Research Papers
These books and research papers provide in-depth analysis and theoretical foundations of cloud hosting.
- Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture by Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood, Ricardo Puttini, and Kiran Fernandes: This book offers a comprehensive overview of cloud computing concepts, technologies, and architectures. It explores various aspects of cloud hosting, including infrastructure, platforms, and applications. [Link: https://www.amazon.com/Cloud-Computing-Concepts-Technology-Architecture/dp/0137025851](https://www.amazon.com/Cloud-Computing-Concepts-Technology-Architecture/dp/0137025851)
- Cloud Computing: Principles and Paradigms by Rajkumar Buyya, Christian Vecchiola, and S. Thamarai Selvi: This book provides a comprehensive understanding of cloud computing principles and paradigms, covering topics such as virtualization, resource management, and service provisioning. It delves into the technical aspects of cloud hosting and its applications. [Link: https://www.amazon.com/Cloud-Computing-Principles-Paradigms-Wiley/dp/0470975381](https://www.amazon.com/Cloud-Computing-Principles-Paradigms-Wiley/dp/0470975381)
- Cloud Computing: A Holistic Approach by Michael J. Shaw: This book offers a holistic perspective on cloud computing, exploring its business, technical, and societal implications. It provides a comprehensive understanding of cloud hosting, its benefits, challenges, and future directions. [Link: https://www.amazon.com/Cloud-Computing-Holistic-Approach-Second/dp/1119054654](https://www.amazon.com/Cloud-Computing-Holistic-Approach-Second/dp/1119054654)
Ending Remarks
As cloud hosting continues to evolve, its impact on the digital landscape will only grow stronger. With its ability to empower businesses with agility, scalability, and security, cloud hosting is poised to remain a cornerstone of modern technology. By understanding its core principles, advantages, and diverse applications, individuals and organizations can leverage its transformative power to achieve their digital goals.
Cloud hosting offers a flexible and scalable platform for businesses of all sizes. When managing data in a cloud environment, understanding character sets and sorting rules is crucial. This is where the SQL `collate` clause comes in handy, allowing you to specify how data is compared and sorted.
For example, you can use the collate sql clause to ensure consistent data ordering across different regions or languages. By leveraging the power of `collate`, you can optimize your cloud database performance and ensure data integrity within your cloud environment.